Level the metal shearing machine. Fill the hydraulic oil tank, open the cover to remove debris, clean the filter screen, and then refill the oil. The type of hydraulic oil to be used depends on the model and region. Turn on the power supply, check the power indicator light, activate all emergency stop switches, start the oil pump, and verify that the motor is rotating in the correct direction. The machine tool operates at a pressure of 25 Mpa. Adjust the machine pressure according to the thickness of the plate. Lubricate the hydraulic shearing machine according to the instructions indicated on the machine's label. If the sheet metal shearing machine suddenly stops working and the blade does not move up or down, first check the machine and oil circuit (solenoid Valve) and foot switch. If no faults are found in the circuit, disassemble the solenoid valve for cleaning. If the two ends of the plate after shearing are inconsistent, check the back gauge Connecting Rod and see if the screws have fallen off or if the synchronous belt is slipping. Adjust the screw of the back gauge guide to bring both ends within the acceptable error range. If the size of the cut material is different from the value displayed on the display, inspect the encoder that connects the flexible shaft to see if it is torn or if the screws are loose. If the connecting flexible shaft is damaged, replace it and then calibrate the value of the back gauge. The machinery produces noise during operation. Check the motor oil pump for any potential noise. Also, check the noise of the oil cylinder and return cylinder. If the machine makes a squeaking sound, check whether the ball head of the return cylinder is low on oil and if the cylinder ball head requires oil. If the pressing cylinder lacks force, add nitrogen at 6-8 MPa. If the blade edge is dull or the blade is not sharp, turn over the blade or it can be replaced in time. When adjusting the blade edge, first set the blade edge clearance to the maximum, then gradually decrease it by closing the ball valve. At this point, the upper and lower blades should be on the same plane. Use a feeler gauge to measure the blade gap between the blade edges and adjust it through the blade-adjusting screws located on the workbench. Symptoms: The edges of the sheared sheet metal are uneven, with burrs or cracks. Symptoms: The edges of the sheared sheet metal are significantly deformed or have irregular cuts. Symptoms: Abnormal noise or vibration occurs during shearing, and the cutting quality is unstable. Symptoms: The shearing machine cannot start or operates unresponsively. Symptoms: Insufficient shearing force, stuttering during shearing, or inability to complete the precision cut. A plate shearing machine is used to cut metal plates into sheets or strips, which is widely used in the sheet metal processing industry. It features a movable upper blade and a fixed lower blade, which are driven by a power device to cut the metal plate at a set gap. The two main types of shearing equipment are hydraulic swing beam and guillotine shearing machines, which vary in blade type and material compatibility. Debugging and troubleshooting of the metal shearing machine encompasses checks of the oil cylinder, oil circuit, and electric back gauge, as well as addressing issues such as noise and blade clearance adjustments in metal fabrication. The quality of the shearing machine also plays a role in the cost of repairs and maintenance and maintaining optimal productivity. By choosing the ADH manufacture, you can benefit from time and cost savings, as well as receive high-quality after-sales service. Contact us for more information about our shearing machines. Gd-Type Diaphragm Compressor,High Power Air Compressor,Propane Gas Compressor,Air Power Air Compressor Permanent Machinery Co., Ltd. , https://www.hjjxcompressor.comI. Commissioning
II. Troubleshooting Hydraulic Shear
1. Oil Circuit:
2. Back Gauge:
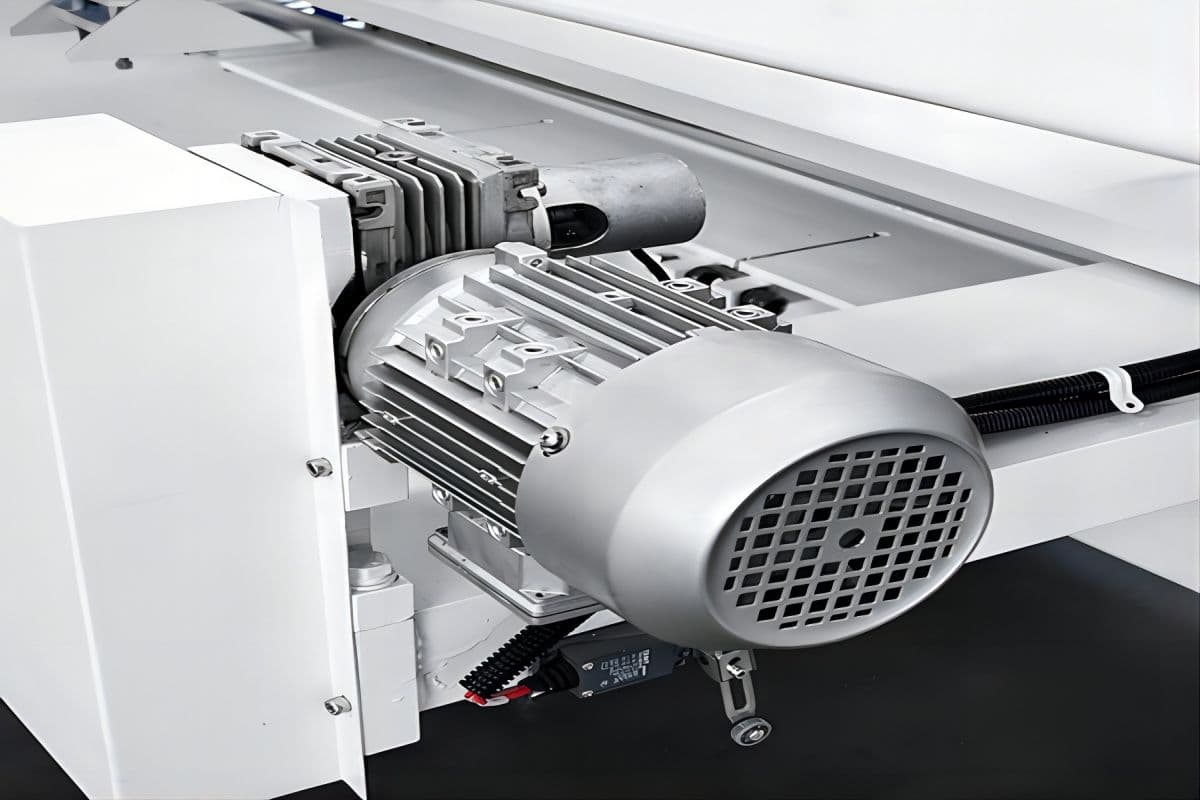

3. Noise
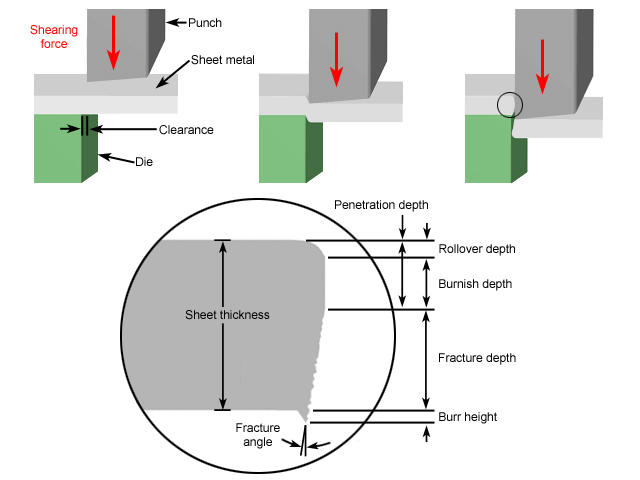
4. Adjustment of Blade Edge Clearance
4.1 Blade Wear
Cause: The blade has been used for a long time, causing the edge to become dull or chipped.
Solution:
4.2 Improper Blade Clearance
Cause: The blade clearance is improperly adjusted, leading to uneven distribution of shearing force.
Solution:
4.3 Incorrect Blade Installation
Cause: The blade is not securely installed or is incorrectly positioned, causing the blade to wobble during shearing.
Solution:

5. Electrical System
Cause: Electrical control system faults, such as broken circuits, poor connections, or controller failures.
Solution:

6. Insufficient Hydraulic System Pressure
Cause: Insufficient hydraulic system pressure or contaminated hydraulic oil.
Solution:
III. What Is Shearing Machine
IV. Preventive MaintenanceÂ
1. Regular Maintenance and Inspections
1.1 Daily Inspections
1.2 Weekly Inspections
1.3 Monthly Inspections
2. Cleaning and Alignment
2.1 Machine Cleaning
2.2 Blade Alignment
3. Professional Maintenance
3.1 When to Seek Professional Help
V. Conclusion